The Importance of the T4 Vertebral Body in Health and Medical Practices
The T4 vertebral body is a vital component of the vertebral column, particularly revered in the field of chiropractic and physical therapy. Understanding its role not only enhances our knowledge of spinal health but also guides practitioners in delivering effective treatments that promote well-being. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the anatomy, functionality, and the implications of the T4 vertebral body in various health practices.
1. Overview of the Vertebral Column
The vertebral column, commonly known as the spine, is comprised of 33 individual vertebrae that are categorized into five regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal. Each region plays a critical role in supporting the body's structure and facilitating movement. The thoracic region, where the T4 vertebral body is located, consists of twelve vertebrae (T1-T12) that articulate with the ribs, contributing to the rib cage and protecting vital organs.
2. Anatomy of the T4 Vertebral Body
The T4 vertebral body is the fourth thoracic vertebra and is uniquely designed to support the upper body's weight while allowing for flexibility and movement. It connects with the second and third thoracic vertebrae above and the fifth thoracic vertebra below, forming a critical part of the thoracic curve.
Key anatomical features of the T4 vertebral body include:
- Vertebral body: This cylindrical structure bears weight and helps support the thoracic spine.
- Pedicles: These are short, thick processes that connect the vertebral body to the vertebral arch, helping to protect the spinal cord.
- Lamina: This flat part of the vertebral arch forms the posterior wall of the spinal canal.
- Spinous process: The bony projection that can be felt through the skin along the back, serving as an attachment point for muscles and ligaments.
3. Functionality of the T4 Vertebral Body
The T4 vertebral body plays several crucial roles in ensuring the proper functioning of the spine. These include:
- Support and Stability: The T4 provides structural support to the thoracic region, which is essential for maintaining posture and balance.
- Mobility: It allows for essential movements such as rotation and flexion of the upper body, which are vital for daily activities.
- Protection: The T4 vertebral body, together with adjacent vertebrae, encases the spinal cord, shielding it from injury.
4. The T4 Vertebral Body in Chiropractic Practices
In the realm of chiropractic care, the T4 vertebral body is of particular interest. Chiropractors are trained to understand the spine's complexity, including how misalignments or subluxations of specific vertebrae can impact overall health.
Common issues associated with the T4 vertebral body include:
- Postural dysfunction: Poor posture can lead to misalignment of the T4, resulting in discomfort and stiffness.
- Neurological issues: Misalignments can affect nerves that exit from the spinal column, potentially causing pain in associated areas.
- Muscle tension: Tension in surrounding muscles due to misalignment can result in chronic pain and discomfort.
4.1 Chiropractic Adjustments
Chiropractors employ a variety of techniques to address issues related to the T4 vertebral body, including spinal adjustments aimed at restoring alignment. Such adjustments can relieve tension, improve mobility, and enhance overall function.
4.2 Techniques Used
Some effective chiropractic techniques concerning the T4 vertebral body are:
- Specific spinal manipulation: Targeted adjustments that aim to correct misalignments.
- Soft tissue therapy: Techniques that relieve muscle tension surrounding the T4 region.
- Mobilization strategies: Gentle movements designed to increase range of motion in the thoracic spine.
5. The T4 Vertebral Body in Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in rehabilitating patients with issues linked to the T4 vertebral body. Physical therapists assess spinal health and create individualized exercise programs that target strength, flexibility, and stability.
5.1 Rehabilitation Exercises
Exercises designed to strengthen the muscles surrounding the T4 vertebral body include:
- Core strengthening: Exercises that engage core muscles can enhance support for the spine.
- Posture correction: Specific drills aimed at promoting better posture can alleviate stress on the T4.
- Flexibility exercises: Stretching protocols focused on the thoracic region to maintain mobility.
5.2 Importance of Posture
Maintaining proper posture not only reduces the risk of injury but also promotes optimal function of the T4 vertebral body. Techniques taught by physical therapists often emphasize:
- Awareness of body alignment: Educating patients about their posture during daily activities.
- Ergonomic practices: Guidance on setting up workspaces to support spinal health.
- Regular movement and stretching: Encouraging breaks and movements to keep the thoracic area mobile.
6. Integrating Health Practices for Spinal Wellness
A comprehensive approach to spinal health involves collaboration between chiropractic and physical therapy practices. By integrating these modalities, patients can experience improved outcomes. Strategies may include:
- Interdisciplinary communication: Regular updates and coordination between chiropractors and physical therapists to optimize treatment plans.
- Education and empowerment: Providing patients with knowledge about their condition and encouraging self-care practices.
- Long-term wellness strategies: Developing maintenance plans that encourage ongoing care and activity for lasting health benefits.
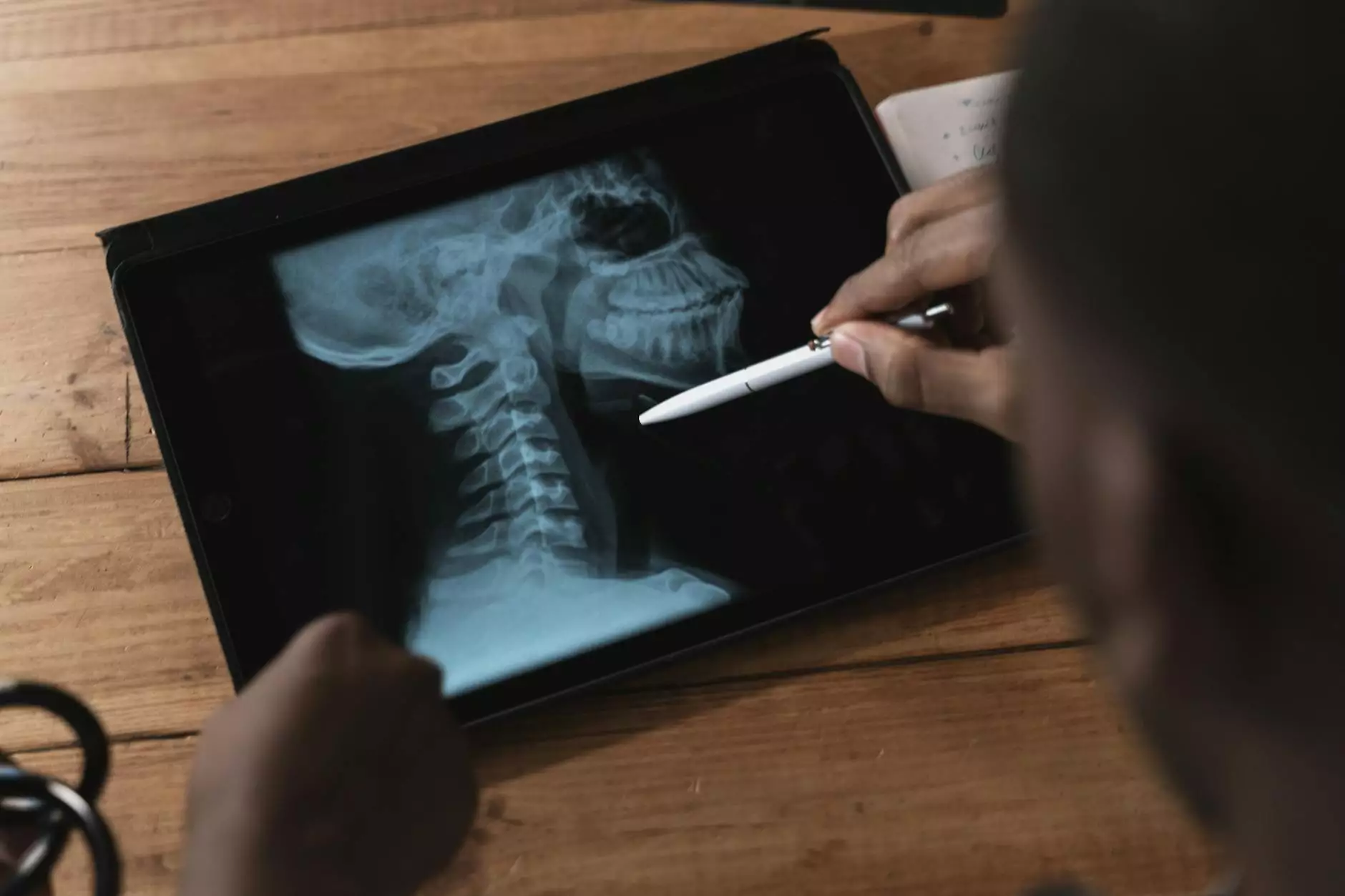
7. The Role of Technology in Understanding the T4 Vertebral Body
Advancements in medical technology have transformed the understanding of spinal health. Imaging techniques such as MRI and CT scans provide detailed insights into the structure and function of the T4 vertebral body, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
7.1 Diagnostic Imaging
Utilizing imaging tools, healthcare professionals can:
- Identify abnormalities: Early detection of conditions related to the T4 vertebral body.
- Plan interventions: Tailoring treatment approaches based on the specific needs of each patient.
- Monitor progress: Assessing the effectiveness of treatments over time.
7.2 Telehealth and Remote Monitoring
With rising advancement in telehealth services, patients can now consult specialists from the comfort of their homes, ensuring continuity in care concerning their T4 vertebral body health. This can include:
- Online consultations: Engaging with healthcare professionals to discuss symptoms and receive guidance.
- Exercise monitoring: Physical therapists can guide patients through exercise programs via video calls.
- Digital health records: Allowing specialists to track patient history and treatment plans more efficiently.
8. Conclusion: Prioritizing Spinal Health and the T4 Vertebral Body
The T4 vertebral body is not only critical in the structure of the spine but also serves as a focal point in both chiropractic care and physical therapy. As we have explored, understanding its anatomy, functionality, and treatment approaches can significantly impact individual health outcomes.
By emphasizing the importance of spinal health through a combination of chiropractic and physical therapy practices, patients can achieve better posture, reduced pain, and enhanced quality of life. Health practitioners should consider the integrated approach as a holistic path to healing, ensuring that the T4 vertebral body—and the entire spine—is well-cared-for and prioritized in the realm of health and wellness.